Why did the Soviet economy fail
Rationing cards and queues, which had become hallmarks of war communism, had disappeared. However, due to prolonged war, low harvests, and several natural disasters the Soviet economy was still in trouble, particularly its agricultural sector.
What kind of economy did the Soviet Union have
The Soviet Union (USSR) was born in 1922 out of the Russian Revolution (1917) and dissolved in 1991. The USSR subscribed to socialist economics roughly based on Marxism.
Was the USSR self sufficient
As such, the Soviet Union's ordinary citizens were generally not allowed access to imported consumer goods, especially those manufactured in the United States. Also known as "the Iron Curtain," the Soviet economic system called for self-sufficiency in all matters, from bread to clothes to cars to fighter aircraft.
What are the weaknesses of the Soviet command economy
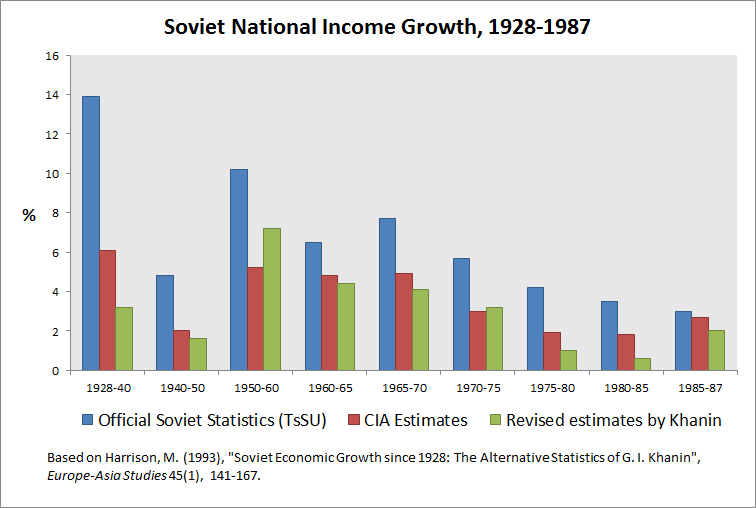
Weakened Soviet economy
They could not commit the expenditure necessary to maintain the arms race. Living standards in the USSR were falling, while in the West they were rising rapidly. Consumer goods were of a much poorer standard as industrial production lagged behind the West.
Why did the Soviet economy grow so fast
How did the USSR succeed in growing so rapidly from 1928 to 1970 In 1928 the country had a small capital stock and a large, ineffectively employed, rural population. The rapid accumulation of capital was the key to rapid growth.
Did the Soviet economy grow
Growth somewhat accelerated in the aftermath of the death of Josef Stalin, but from the 1960s onward the rates of economic growth began to fall, declining continuously throughout the rest of the Soviet period down to near zero just before the dissolution of the USSR at the end of 1991.
Why did the Soviet system became so weak and why did the economy stagnant
The economy of the Soviet Union became stagnant. The Soviet economy used much of its resources in maintaining a nuclear and military arsenal. The Soviet Union too became stagnant due to rampant corruption, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land.
How did people get paid in USSR
Throughout the Stalinist period, most Soviet workers had been paid for their work based on a piece-rate system. Thus their individual wages were directly tied to the amount of work they produced. This policy was intended to encourage workers to toil and therefore increase production as much as possible.
Was the Soviet Union a poor country
During the Revolution, and for much of the following two decades, to be poor – in theory, at least – was to be politically admirable. The Soviet Union was a very poor country indeed.
How much of the USSR was in poverty
If we settle for a poverty threshold of 60 roubles in 1978 (A minimum budget for that year), then a sociological study carried out by Soviet economists finds that 23% of the population was poor (Sample size of 62000 family budgets, towns of origin not specified).
What were the advantages and disadvantages of the Soviet planned economy
Command economy advantages include low levels of inequality and unemployment and the common objective of replacing profit as the primary incentive of production. Command economy disadvantages include lack of competition, which can lead to a lack of innovation and lack of efficiency.
Does Russia have a weak economy
It has enormous natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. It is the world's eleventh-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the sixth-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). Due to a volatile currency exchange rate, Russia's GDP as measured in dollars fluctuates sharply.
Did the USSR have the biggest economy
In 1970, the Soviet nominal GDP reached $1.24 trillion, which was the world's second largest national economy by nominal GDP at the time. By 1983, the Soviet nominal GDP had grown to circa $4.2 trillion, rivaling that of the United States, which shocked the entire world.
When did Russia’s economy improve
Between 2000 and 2002, significant pro-growth economic reforms included a comprehensive tax reform, which introduced a flat income tax of 13%; and a broad effort at deregulation which benefited small and medium-sized enterprises. Between 2000 and 2008, Russian economy got a major boost from rising commodity prices.
Why did the USSR grow so fast
How did the USSR succeed in growing so rapidly from 1928 to 1970 In 1928 the country had a small capital stock and a large, ineffectively employed, rural population. The rapid accumulation of capital was the key to rapid growth.
Did the economy improve under Stalin
They argue that although excessively brutal, Stalin's policies allowed Russia to develop a strong modern economy that sustained a successful war effort in 1941-1945 and propelled the Soviet Union into a dominant power after WWII.
Did the USSR reduce poverty
The USSR managed to reduce inequality and poverty with respect to pre-revolutionary times, and it did deliver in bringing a level of equality comparable to that of Nordic social democracies.
Who were rich farmers in USSR
kulak
kulak, (Russian: “fist”), in Russian and Soviet history, a wealthy or prosperous peasant, generally characterized as one who owned a relatively large farm and several head of cattle and horses and who was financially capable of employing hired labour and leasing land.
How much money did the US give the USSR
$11 billion
In total, the U.S. deliveries to the USSR through Lend-Lease amounted to $11 billion in materials ($180 billion in the 2020 money value): over 400,000 jeeps and trucks; 12,000 armored vehicles (including 7,000 tanks, about 1,386 of which were M3 Lees and 4,102 M4 Shermans); 11,400 aircraft (of which 4,719 were Bell P- …
What countries broke free from USSR
Bush recognized all 12 independent republics and established diplomatic relations with Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia and Kyrgyzstan. In February 1992, Baker visited the remaining republics and diplomatic relations were established with Uzbekistan, Moldova, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and Tajikistan.
Was the USSR the richest country
The Soviet Union was the second richest country in the world. The Russian Federation is the eleventh richest country in the world. Apart from the loss of the other republics, what happened to all that Soviet economic and industrial might
Why are former USSR countries poor
Following the dissolution, market forces overwhelmed a state that had virtually no market involvement for almost 70 years. In addition, funding for government-provided services declined, which left many people without the resources to survive.
What were the positive features of the Soviet system
Answer: The three positive features of the Soviet system were : The Soviet economy was more developed than the rest of the world except the US. It had a complex communication network, vast energy resources, machinery production and a transport system that connected its remotest areas.
How was Soviet economy different from capitalist economy
[1] Answer: The Soviet economy was planned and controlled by the state only whereas the capitalist economy was enjoyed by the people or group of people as well as by the state.
Is Russia’s economy rich or poor
In 2013, the World Bank announced that Russia had graduated to a high-income economy based on the results of 2012 but in 2016 it was reclassified as an upper-middle income economy due to changes in the exchange rate of the Russian ruble, which is a floating currency.


