What is the ɪ sound in phonetics
To make the /ɪ/ sound:
The /ɪ/ vowel is a high-front sound. Your tongue should be positioned high in your mouth, and shifted toward the front. Your lips should be relaxed, and only slightly open. Vibrate your vocal cords with your mouth in this position.
What type of sound is ɪ
Vowel sound
The /ɪ/ sound is a Vowel sound and it's technical name is the 'Near-Close Near-Front Unrounded Vowel'. Remember that the key to pronunciation s physical and the name tells us about how the sound is made physically.
What is an example of a vowel sound i :/
LONG VOWEL SOUND /i:/
Examples of words containing this /i:/ sound are bee, need, machine, kerosene, sea, receive, we, these, seize, be, free, tree, ceiling, glee, margarine, Peter, beans, seem, beat, leaf, deceive, people, quay, key, eat, meet, leaf, cheek, etc.
What are examples of E sound words
bed, beg, fed, gem, get, hen, hem, jet, led, leg, let, men, met, net, pen, peg, pet, red, set, ten, yet, wet. The following diagram shows some examples of short E and long E words. Scroll down the page for more examples and stories using the short E and long E words.
What sound is tʃ and ʃ
With /tʃ/ the air is released suddenly like a sneeze, making it almost impossible to extended the sound for any length of time. In contrast, you can extended /ʃ/ virtually as long as you like, as people do when they really want someone to be quiet.
What is the sound tʃ and dʒ
These two are pronounced with exactly the same mouth position but /dʒ/ uses the voice, whereas /tʃ/ is just a sudden puff of air similar to a sneeze.
What is the tʃ sound
So what is an affricate. Sound the affricates are made by first stopping the Airstream. And then releasing it through a narrow passage in your mouth. With an audible friction.
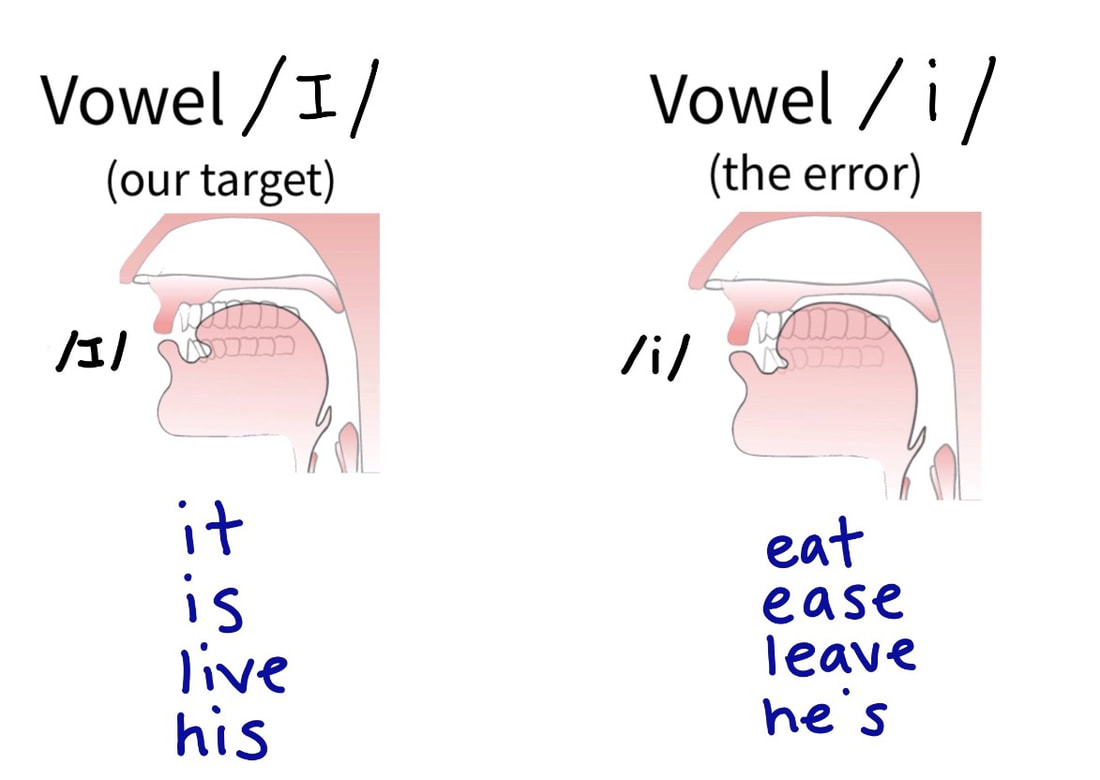
What is the difference between ɪ and i
Difference Between i and i:
/i:/ is a longer sound like EE – try saying 'seem': did you notice the front tip of the tongue rising higher towards the tooth ridge /ɪ/ is a short sound – try saying 'sim', the front tip of the tongue lowers a little bit.
What is the difference between ʊ and u
It is similar to the /u:/ sound, but it is shorter. /ʊ/ not /u:/. To produce the ʊ sound put your tongue close to the top and near the back of your mouth and make a short voiced sound with your mouth closed.
What are the 3 sounds of E
There are three common sounds using the letter E. The ee sound is used with the front part of the mouth, the eh sound is used with the middle portion of the mouth, and the er sound is used with the rear portion of the mouth. Here are some words that come from the front of the mouth using the sound ee.
How do you pronounce ə
The symbol /ə/ (an upside down 'e') is used in the dictionary to show the most common weak vowel in English, which is pronounced as a relaxed 'uh'. /ə/ is called 'schwa'. So you probably saw the symbol /ə/ in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) in your dictionary.
Is it ʃ or tʃ
The sounds /tʃ/ and /ʃ/ are both voiceless, alveo-palatal consonants. However, /tʃ/ is an affricate while /ʃ/ is a fricative. When you pronounce /tʃ/, the air in your mouth should stop (like a /t/) before it is released (like a /ʃ/).
What does ʧ sound like in English
/ʧ/ is pronounced without your tongue moving and with more air released than with /t/. It is similar to the sound of a sneeze, and the air released should be able to move a piece of paper or be felt on your hand five centimetres in front of your mouth.
What is the ː in linguistics
IPA. In the International Phonetic Alphabet the sign ː (not a colon, but two triangles facing each other in an hourglass shape; Unicode U+02D0 ) is used for both vowel and consonant length. This may be doubled for an extra-long sound, or the top half (ˑ) may be used to indicate that a sound is "half long".
What is the symbol ɪ called
Handbook of the International Phonetic Association defines [ɪ] as a mid-centralized (lowered and centralized) close front unrounded vowel (transcribed [i̽] or [ï̞]), and the current official IPA name of the vowel transcribed with the symbol ⟨ɪ⟩ is a near-close near-front unrounded vowel.
What is the meaning of ʊ
The letter Ʊ (minuscule: ʊ), called horseshoe or sometimes bucket, inverted omega or latin upsilon, is a letter of the International Phonetic Alphabet used to transcribe a near-close near-back rounded vowel.
What vowel is ʊ
/ʊ/is a high, back, lax vowel. To make it, your tongue should be lifted high in the mouth (slightly lower than /u/), and shifted toward the back.
What is the difference between E and ɛ sound
As you can see, these vowels are identical, except that the tongue is a little higher for /e/ than it is for /ɛ/.
What is the difference between ə and ɜ
And first of all it's a long vowel as well that's a distinction. So it's a longer sound and when i make the er. Sound my tongue is also less relaxed it's a bit tighter. Than the sound on the left.
How do you pronounce ƏƱ
The /əʊ/ symbol is made up of the short vowel sounds /ə/ and /ʊ/, meaning your mouth moves from the totally relaxed or slack mouth position of /ə/ to the rounded position of /ʊ/ while the /əʊ/ sound is made.
What does ɒ sound like
It's right at the bottom and it's pulled back this is rounded which means that your lips are in a round shape. They're not stretched out oh say it after me. Oh. Oh and now some words with this sound.
What is ʧ called
It is a sound from the 'Consonants Pairs' group and it is called 'Voiceless palato- alveolar affricate'.
When to use ʃ or ʒ
These sounds exist in many parts of Latin America). /ʃ/ is the sound we make when we want to ask for silence (Shhhh…!) and /ʒ/ is its voiced counterpart.
What is the aɪ sound in English
/ɑɪ/ is a diphthong, which is a combination of two different vowel sounds. To begin, place your tongue low in your mouth, and shifted toward the back, to say /ɑ/. Then, as you vibrate your vocal cords, lift your tongue high in the mouth and shift it forward, to say /ɪ/.
What is Ʃ vs tʃ
The sounds /tʃ/ and /ʃ/ are both voiceless, alveo-palatal consonants. However, /tʃ/ is an affricate while /ʃ/ is a fricative. When you pronounce /tʃ/, the air in your mouth should stop (like a /t/) before it is released (like a /ʃ/).


